Publications
Publications of Our Group.
2025
- T-RO
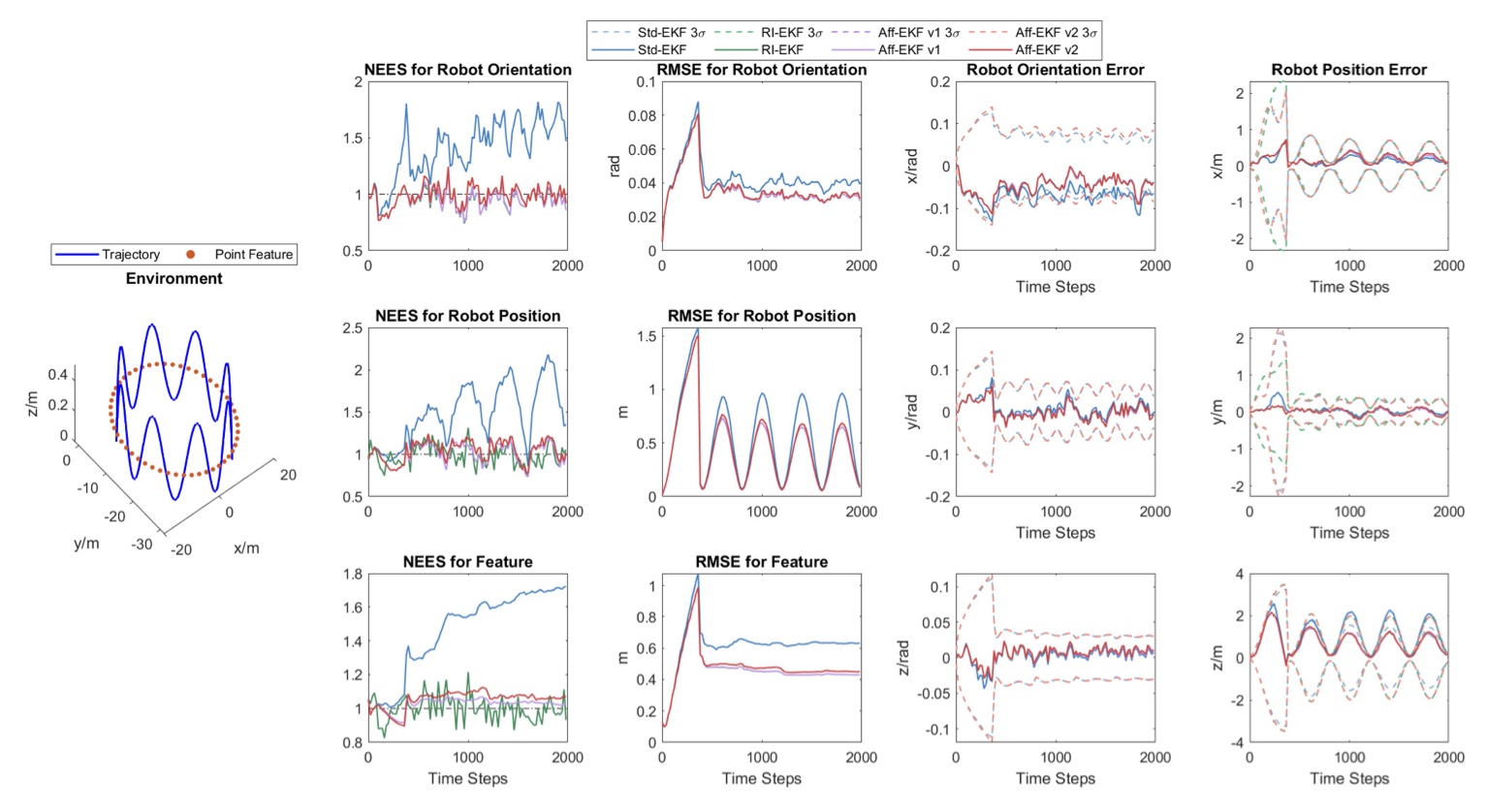 Affine EKF: Exploring and Utilizing Sufficient and Necessary Conditions for Observability Maintenance to Improve EKF ConsistencyYang Song, Liang Zhao, and Shoudong HuangIEEE Transactions on Robotics, 2025
Affine EKF: Exploring and Utilizing Sufficient and Necessary Conditions for Observability Maintenance to Improve EKF ConsistencyYang Song, Liang Zhao, and Shoudong HuangIEEE Transactions on Robotics, 2025Inconsistency issue is one crucial challenge for the performance of extended Kalman filter (EKF) based methods for state estimation problems, which is mainly affected by the discrepancy of observability between the EKF model and the underlying dynamic system. In this work, some sufficient and necessary conditions for observability maintenance are first proved. We find that under certain conditions, an EKF can naturally maintain correct observability if the corresponding linearization makes unobservable subspace independent of the state values. Based on this theoretical finding, a novel affine EKF (Aff-EKF) framework is proposed to overcome the inconsistency of standard EKF (Std-EKF) by affine transformations, which not only naturally satisfies the observability constraint but also has a clear design procedure. The advantages of our Aff-EKF framework over some commonly used methods are demonstrated through mathematical analyses. The effectiveness of our proposed method is demonstrated on three simultaneous localization and mapping (SLAM) applications with different types of features, typical point features, point features on a horizontal plane and plane features. Specifically, following the proposed procedure, the naturally consistent Aff-EKFs can be explicitly derived for these problems. The consistency improvement of these Aff-EKFs are validated by Monte Carlo simulations.
- IROS
 Correspondence-Free Multiview Point Cloud Registration via Depth-Guided Joint OptimisationYiran Zhou, Yingyu Wang, Shoudong Huang, and Liang ZhaoIn IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems, 2025
Correspondence-Free Multiview Point Cloud Registration via Depth-Guided Joint OptimisationYiran Zhou, Yingyu Wang, Shoudong Huang, and Liang ZhaoIn IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems, 2025Multiview point cloud registration is a fundamental task for constructing globally consistent 3D models. Existing approaches typically rely on feature extraction and data association across multiple point clouds; however, these processes are challenging to obtain global optimal solution in complex environments. In this paper, we introduce a novel correspondence-free multiview point cloud registration method. Specifically, we represent the global map as a depth map and leverage raw depth information to formulate a non-linear least squares optimisation that jointly estimates poses of point clouds and the global map. Unlike traditional feature-based bundle adjustment methods, which rely on explicit feature extraction and data association, our method bypasses these challenges by associating multi-frame point clouds with a global depth map through their corresponding poses. This data association is implicitly incorporated and dynamically refined during the optimisation process. Extensive evaluations on real-world datasets demonstrate that our method outperforms state-of-the-art approaches in accuracy, particularly in challenging environments where feature extraction and data association are difficult.
- T-RO
 Occupancy-SLAM: An Efficient and Robust Algorithm for Simultaneously Optimizing Robot Poses and Occupancy MapYingyu Wang, Liang Zhao, and Shoudong HuangIEEE Transactions on Robotics, 2025
Occupancy-SLAM: An Efficient and Robust Algorithm for Simultaneously Optimizing Robot Poses and Occupancy MapYingyu Wang, Liang Zhao, and Shoudong HuangIEEE Transactions on Robotics, 2025Joint optimization of poses and features has been extensively studied and demonstrated to yield more accurate results in feature-based SLAM problems. However, research on jointly optimizing poses and non-feature-based maps remains limited. Occupancy maps are widely used non-feature-based environment representations because they effectively classify spaces into obstacles, free areas, and unknown regions, providing robots with spatial information for various tasks. In this paper, we propose Occupancy-SLAM, a novel optimization-based SLAM method that enables the joint optimization of robot trajectory and the occupancy map through a parameterized map representation. The key novelty lies in optimizing both robot poses and occupancy values at different cell vertices simultaneously, a significant departure from existing methods where the robot poses need to be optimized first before the map can be estimated. This paper focuses on 2D laser-based SLAM to investigate how to jointly optimize robot poses and the occupancy map. In our formulation, the state variables in optimization include all the robot poses and the occupancy values at discrete cell vertices in the occupancy map. Moreover, a multi-resolution optimization framework that utilizes occupancy maps with varying resolutions in different stages is introduced. A variation of Gauss-Newton method is proposed to solve the optimization problem at different stages to obtain the optimized occupancy map and robot trajectory. The proposed algorithm is efficient and converges easily with initialization from either odometry inputs or scan matching, even when only limited key-frame scans are used. Furthermore, we propose an occupancy submap joining method, enabling more effective handling of large-scale problems by incorporating the submap joining process into the Occupancy-SLAM framework. Evaluations using simulations and practical 2D laser datasets demonstrate that the proposed approach can robustly obtain more accurate robot trajectories and occupancy maps than state-of-the-art techniques with comparable computational time. Preliminary results in the 3D case further confirm the potential of the proposed method in practical 3D applications, achieving more accurate results than existing methods.
- TASE
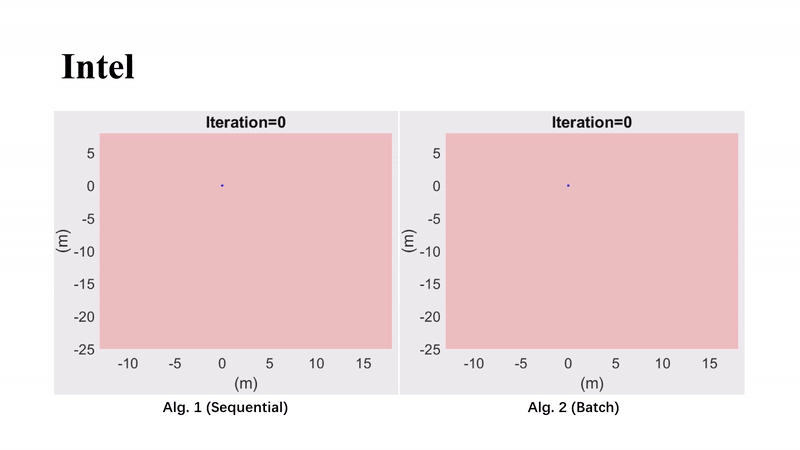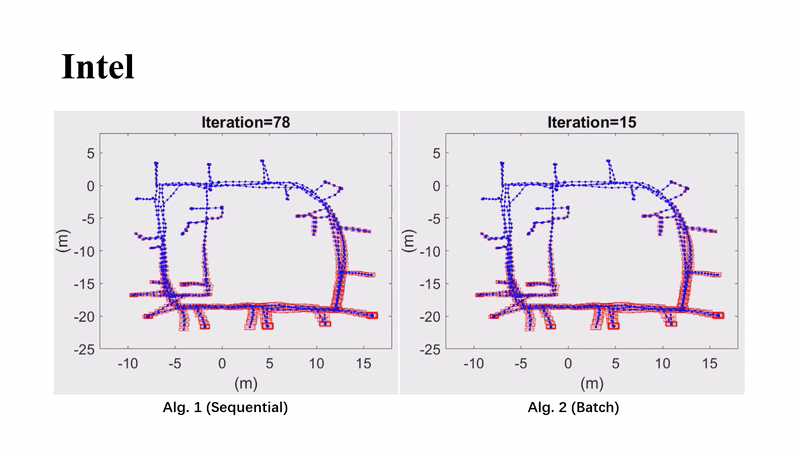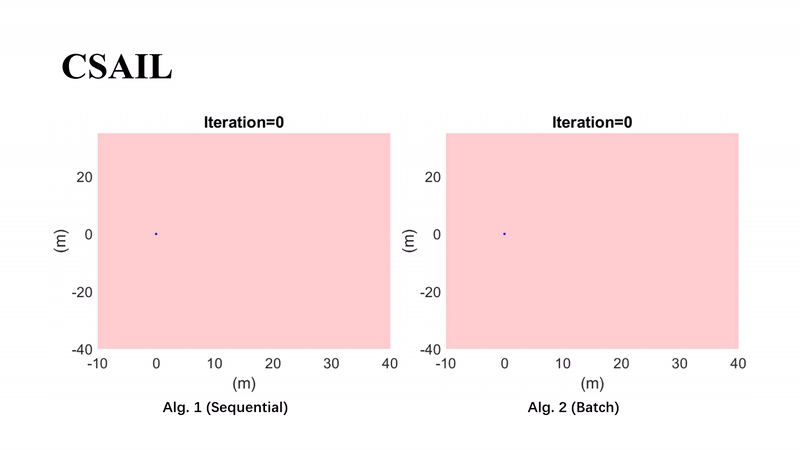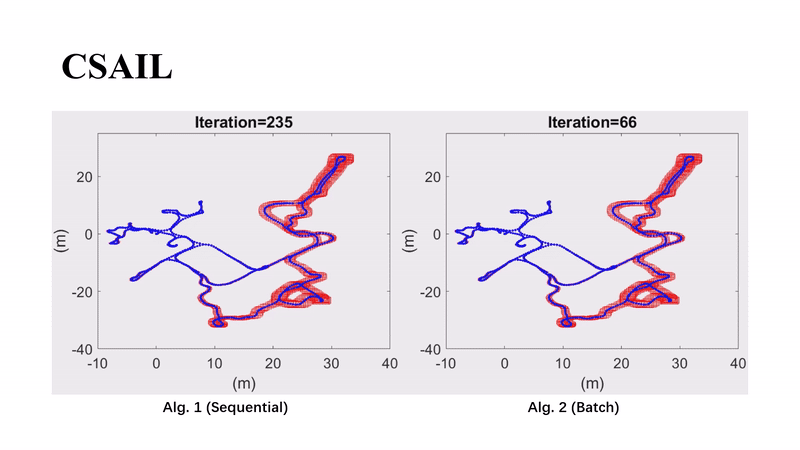 Guaranteed 2D Pose Graph SLAM With Bounded Noises: An Efficient Interval ApproachYang Song, Heng Yang, Liang Zhao, and Shoudong HuangIEEE Transactions on Automation Science and Engineering, 2025
Guaranteed 2D Pose Graph SLAM With Bounded Noises: An Efficient Interval ApproachYang Song, Heng Yang, Liang Zhao, and Shoudong HuangIEEE Transactions on Automation Science and Engineering, 2025This paper focuses on developing a performance guaranteed state estimation algorithm for 2D pose graph problems for mobile robots. Different from probabilistic methods, the measurement noises are only assumed to be bounded without any prior knowledge about their distributions. Based on the interval analysis, we first propose a vanilla sequential contractor that iteratively uses edge-wise noise bounds to contract pose intervals at the nodes, which can provide the guaranteed feasible domains that contain the ground-truth values. Then, to improve the efficiency in solving large-scale pose graphs, an efficient batch contractor is developed by improving the update order and exploiting a relaxation of the nonlinear measurement functions. The effectiveness and efficiency of our approaches are validated on simulated and real-world datasets.
- ICRA
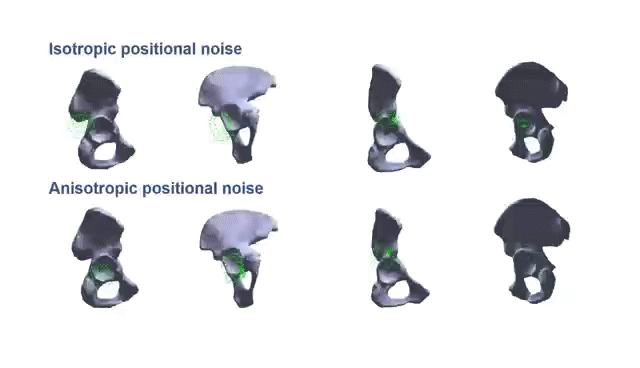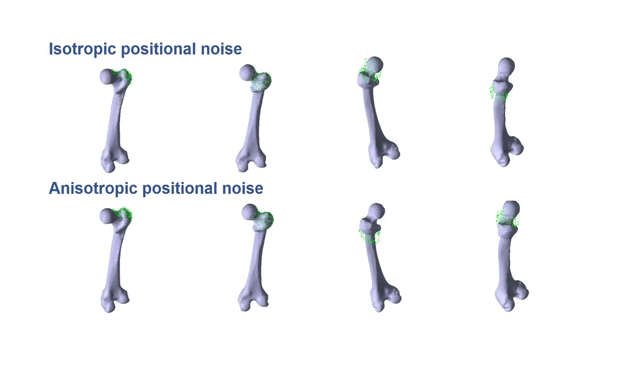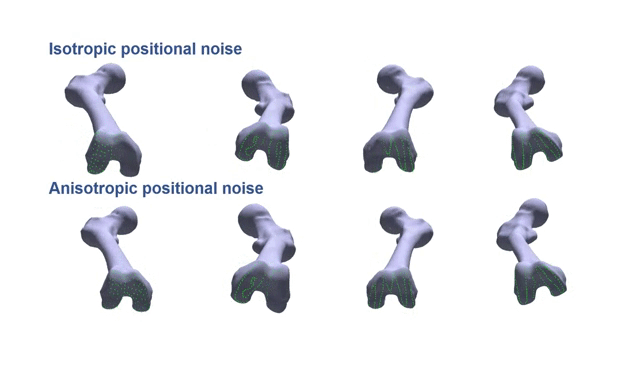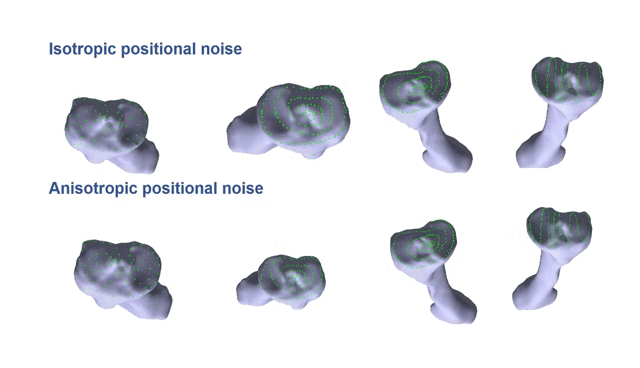 Partial-to-Full Registration based on Gradient-SDF for Computer-Assisted Orthopedic SurgeryTiancheng Li, Peter Walker, Danial Hammoud, Liang Zhao, and Shoudong HuangIn IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation, 2025
Partial-to-Full Registration based on Gradient-SDF for Computer-Assisted Orthopedic SurgeryTiancheng Li, Peter Walker, Danial Hammoud, Liang Zhao, and Shoudong HuangIn IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation, 2025In computer-assisted orthopedic surgery (CAOS), accurate pre-operative to intra-operative bone registration is an essential and critical requirement for providing navigational guidance. This registration process is challenging since the intraoperative 3D points are sparse, only partially overlapped with the pre-operative model, and disturbed by noise and outliers. The commonly used method in current state-of-the-art orthopedic robotic system is bony landmarks based registration, but it is very time-consuming for the surgeons. To address these issues, we propose a novel partial-to-full registration framework based on gradient-SDF for CAOS. The simulation experiments using bone models from publicly available datasets and the phantom experiments performed under both optical tracking and electromagnetic tracking systems demonstrate that the proposed method can provide more accurate results than standard benchmarks and be robust to 90% outliers. Importantly, our method achieves convergence in less than 1 second in real scenarios and mean target registration error values as low as 2.198 mm for the entire bone model. Finally, it only requires random acquisition of points for registration by moving a surgical probe over the bone surface without correspondence with any specific bony landmarks, thus showing significant potential clinical value.
2024
- IROS
 Grid-based Submap Joining: An Efficient Algorithm for Simultaneously Optimizing Global Occupancy Map and Local Submap FramesYingyu Wang, Liang Zhao, and Shoudong HuangIn IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems, 2024
Grid-based Submap Joining: An Efficient Algorithm for Simultaneously Optimizing Global Occupancy Map and Local Submap FramesYingyu Wang, Liang Zhao, and Shoudong HuangIn IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems, 2024In this paper, we first formulate the 2D grid-based submap joining problem as a non-linear least squares (NLLS) form to optimize the global occupancy map and local submap frames simultaneously. We then prove that in solving the NLLS problem using Gauss-Newton (GN) method, the increments of the poses in each iteration are independent of the occupancy values of the global occupancy map. Based on this property, we propose a pose-only GN algorithm equivalent to full GN method to solve the NLLS problem. The proposed submap joining algorithm is very efficient due to the independent property and the pose-only solution. Evaluations using simulations and publicly available practical 2D laser datasets confirm the outperformance of our proposed method compared to the state-of-the-art methods in terms of efficiency and accuracy, as well as the ability to solve the grid-based SLAM problem in very large-scale environments.